LCC/LCA/S-LCA¶
General Description¶
At the end of their lifecycle, products tend to exhibit greater uniformity compared to their initial manufacturing stage, making the processes of disassembly, sorting, and separation more challenging to automate. Assessing their condition typically requires manual inspection and subsequent treatment based on the extent of damage or wear they have endured. AI presents numerous opportunities to optimize the material circulation infrastructure in the economy, particularly by leveraging algorithms capable of object recognition and identification using cameras and sensors.
The next phase involves conducting an impact analysis on various end-of-life scenarios for different machinery. This analysis takes into account cost (Life Cycle Cost), environmental (Life Cycle Assessment), and social (Social Life Cycle Assessment) perspectives. AI algorithms are employed to model the disassembly and recycling processes, predicting the outcomes of each action by examining the probabilistic relationships among disassembly, sorting, separation, and recycling aspects. Based on the results obtained from Life Cycle Cost, Life Cycle Assessment, and Social Life Cycle Assessment, the algorithms formulate a multi-objective optimization strategy that balances economic, social, and environmental benefits.
The development of a data-driven model enables the identification of the most suitable end-of-life approach for the old machine, considering factors such as energy consumption, safety level, maintainability, productivity, and technological advancements. This endeavor involves integrating AI technologies associated with Visual Recognition and Machine Learning.
Usage Viewpoint¶
Use Model¶
Description¶
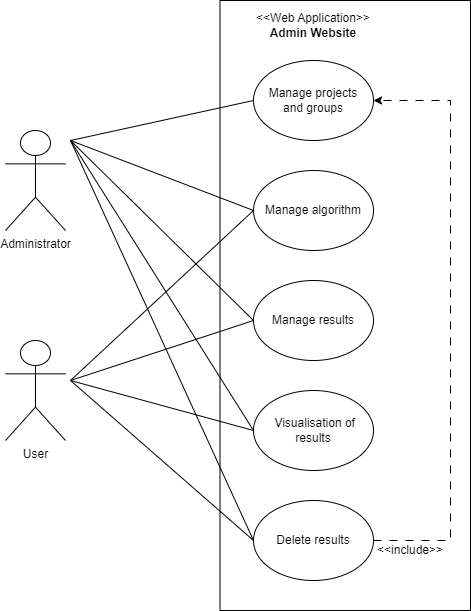
Within the business context, the AI-LC solution serves as a valuable disassembly support tool. This system incorporates an artificial intelligence algorithm that assists operators during the disassembly phase. The algorithm relies on input data derived from a range of analyses, including Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Life Cycle Costing (LCC), Social Life Cycle Assessment (S-LCA), and the product’s bill of materials (BOM).
Prior to initiating the processing, the disassembly process operator conducts the necessary analyses and uploads the corresponding data into the AI-LC system. Once logged in with their personal account (provided by the administrator), the operator awaits the algorithm to perform its analysis. The algorithm then generates an optimal sequence for the efficient and effective disassembly of all product components.
By leveraging AI capabilities, the AI-LC solution streamlines the disassembly process, enabling operators to make informed decisions and optimize the overall efficiency of disassembly operations.
Identification¶

Information¶

Parameters¶

How to create a new analysis¶
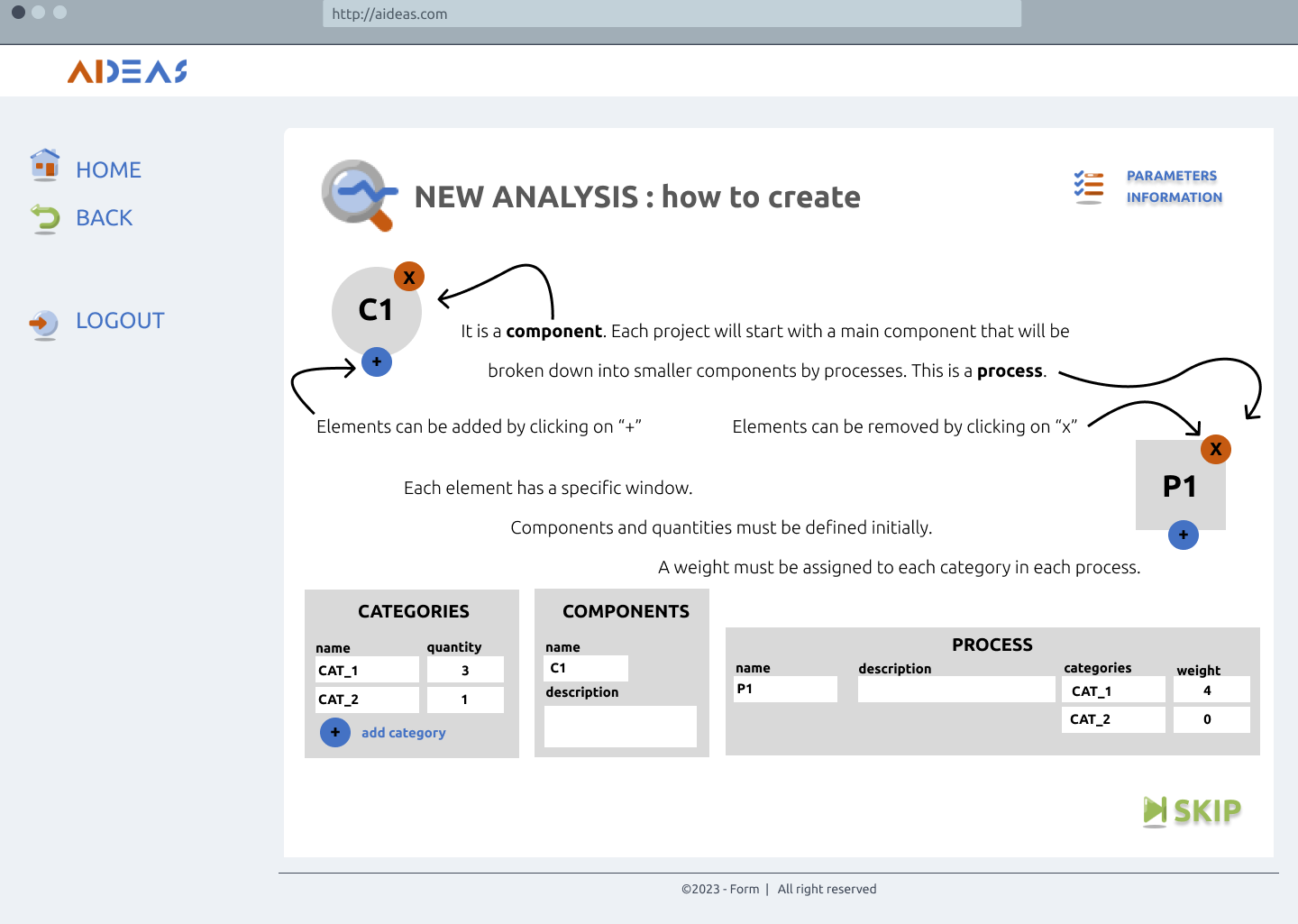
Create a new analysis¶
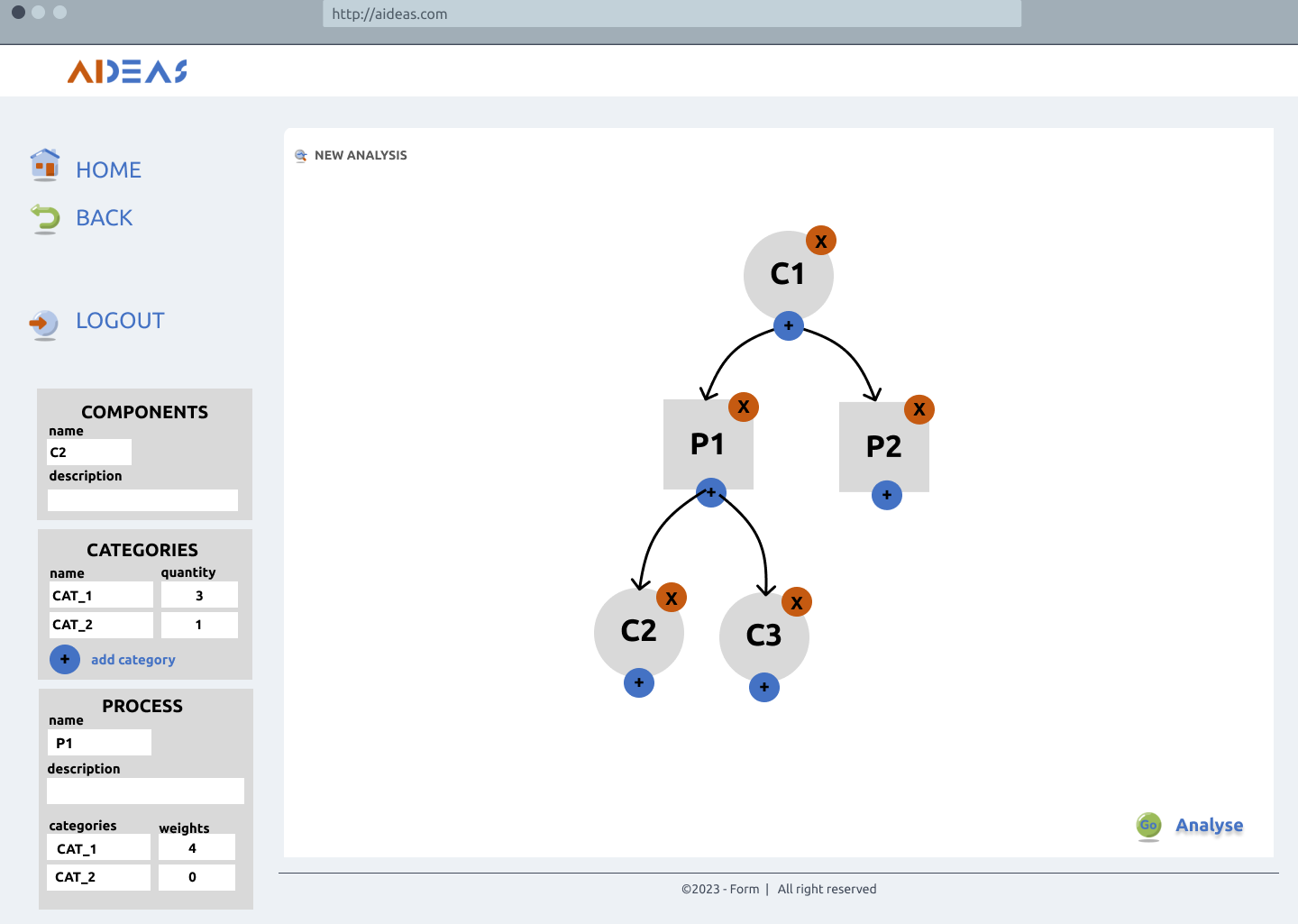
Analysis solution¶
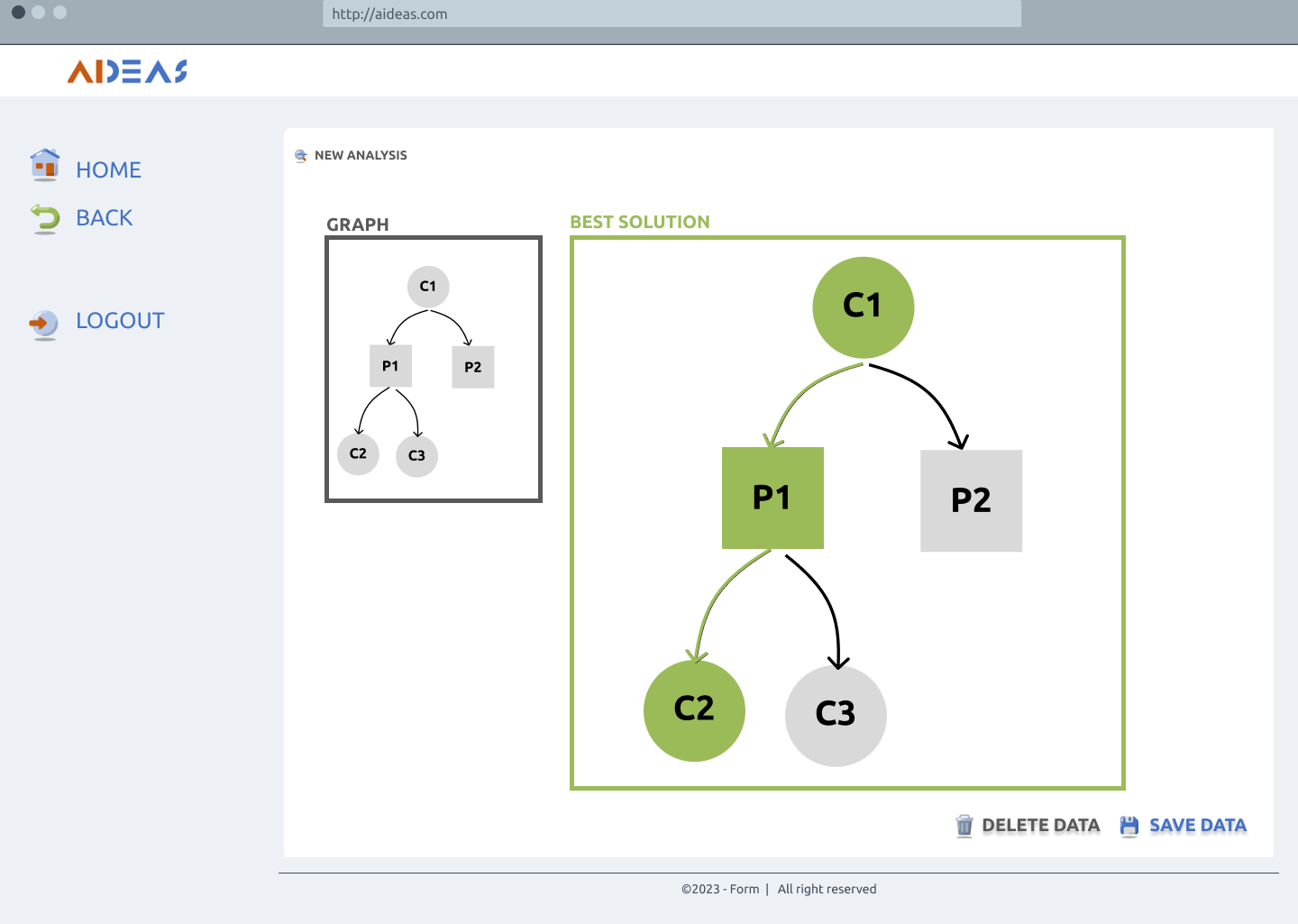
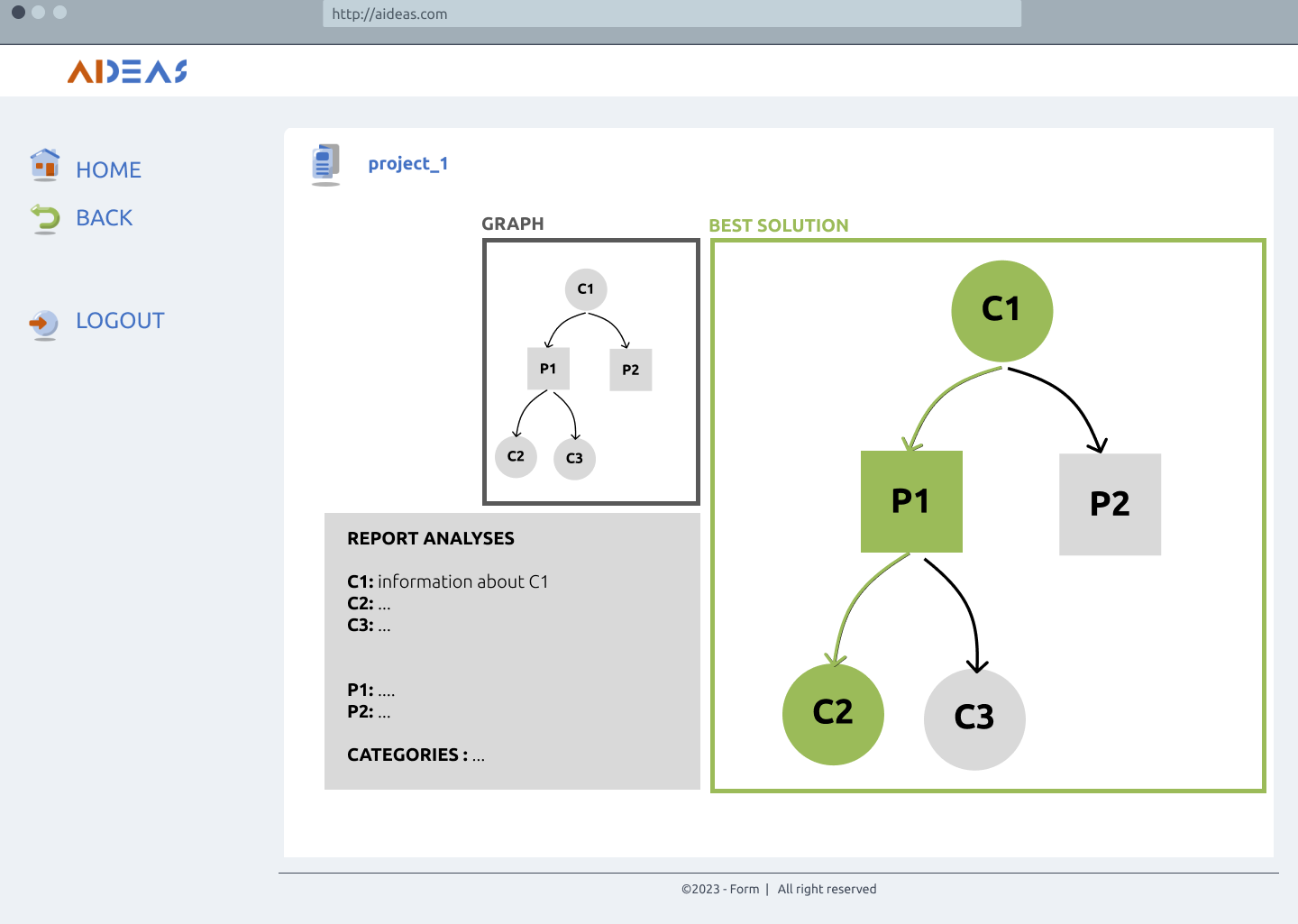
Report analyses¶
Old analyses¶
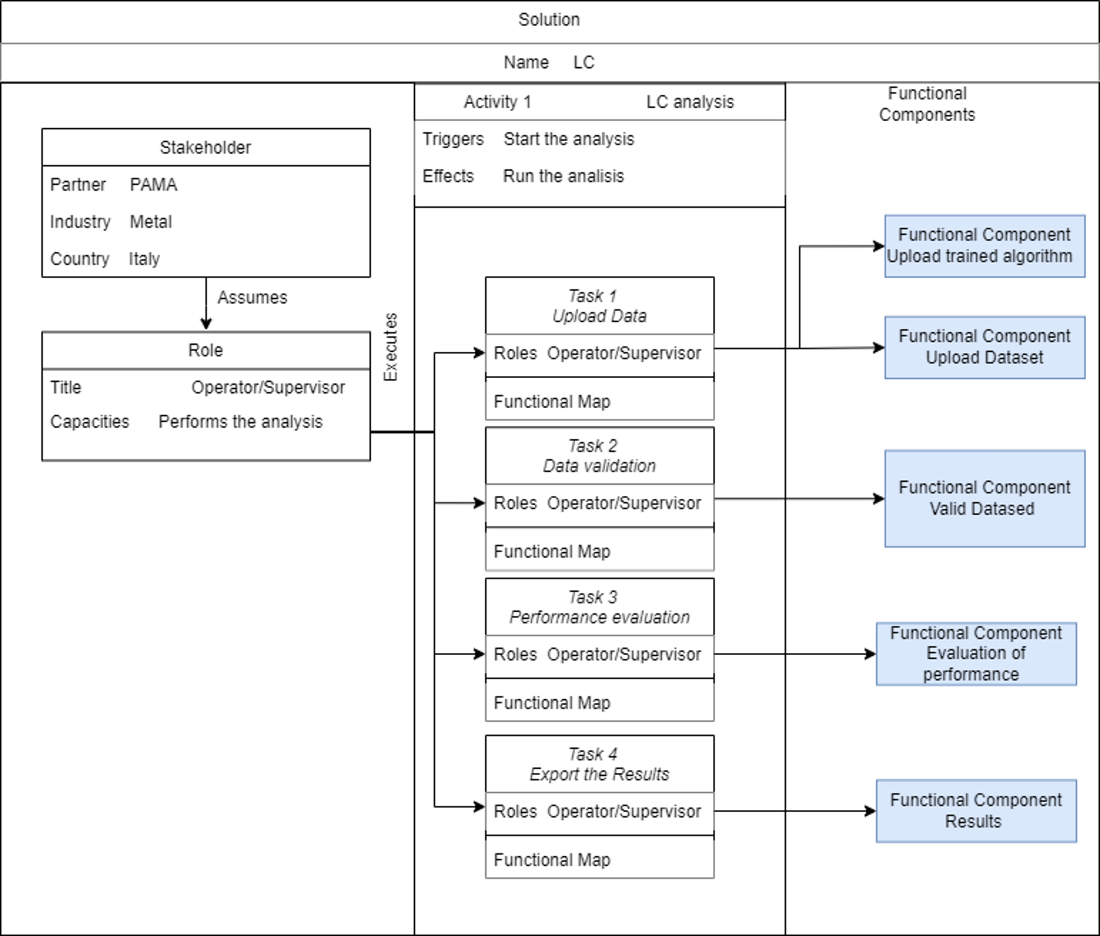
Usage activity diagram¶
The following image shows the interaction between different tasks and roles. This diagram illustrates the dynamic flow of interactions, offering a representation of the activities performed by the solution and providing a clear understanding of the activities performed with the AILC solution.
Functional Viewpoint¶
Functional diagram¶
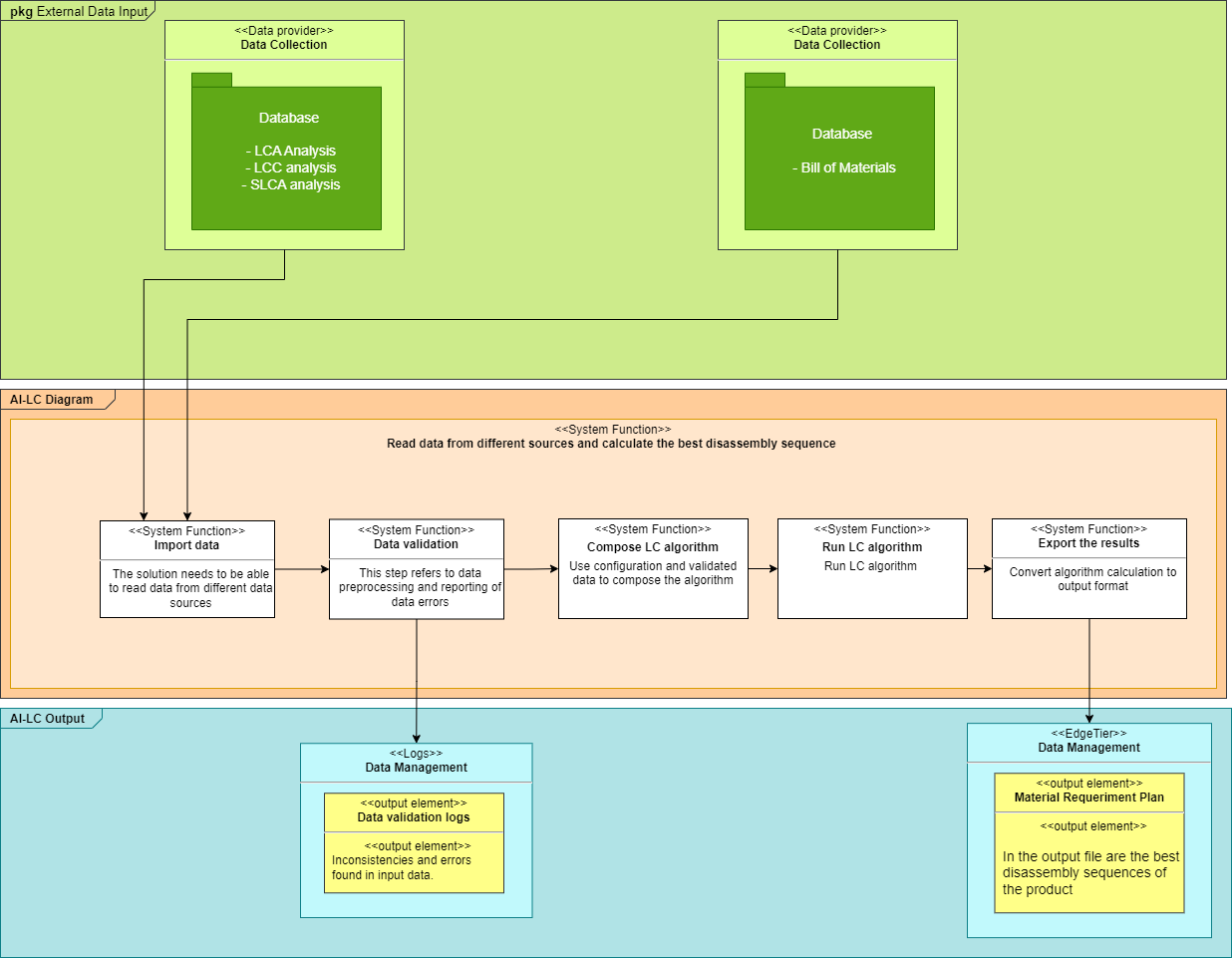
Functional description¶
What: The main feature of this component is to identify the best disassembly choice considering several parameters such as LCA, LCC, SLCA analyses previously performed on the assembly.
Who: Production managers. Maintenance operators
Where: Various products
Why: The purpose of this component is to be a support to the operator who disassembles the product. In fact, this algorithm will help him to be more productive by supporting him in choosing the end-of-life of the product.
Input and output data for each component¶
Import Data¶
Inputs:
LCA Analysis: Analysis previously performed on each individual component of the assembly.
LCC analysis: Analysis previously performed on each individual component of the assembly.
SLCA analysis: Analysis previously performed on each individual component of the assembly.
BOM: Product Bill of Materials.
Outputs:
Data ready to use.
Data Validation¶
Inputs:
Data ready to use
Outputs:
Input data are checked and if they are incorrect, a warning message is returned.
Compose LC Algorithm¶
Inputs:
Data ready to use
Outputs:
Algorithm ready to perform the analysis.
Run LC Algorithm¶
Inputs:
Data ready to use
Algorithm ready to use
Outputs:
Raw data output: the output of the algorithm represents the best sequence of product disassembly, considering the different analyses given as input.
Export the result¶
Inputs:
Raw data output
Outputs:
Data output: The output data is organized within a file so that it can be easily accessed. The file format has yet to be defined.
Software requirements¶
Software Component |
Description/Role |
Required Version/Configuration |
Dependencies |
|---|---|---|---|
Linux OS or Windows OS |
Operating system needed to use the tool |
||
Docker |
Build, share and run containers |
latest |
N/A |
Lifecycle¶
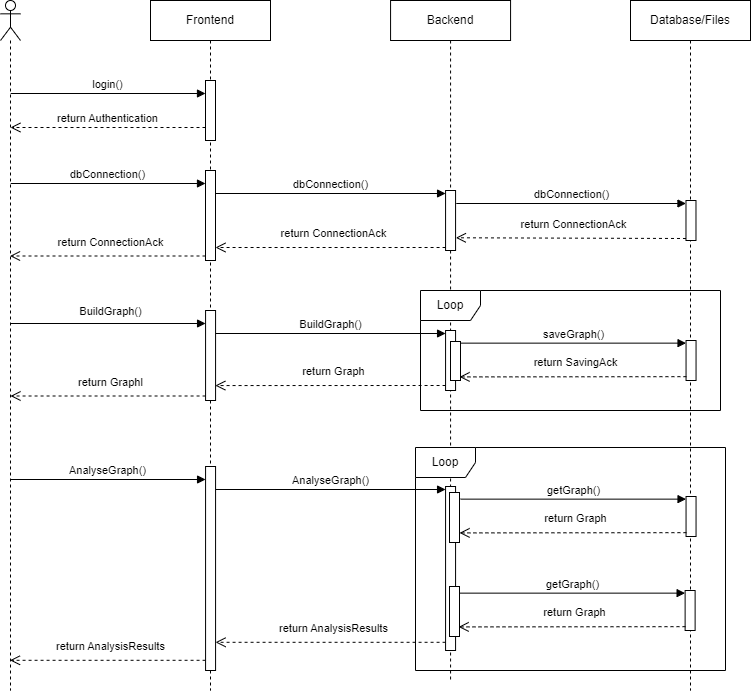
This sequence diagram illustrates the flow of interactions between the User, Frontend, Backend, and Data/Files objects during the main processes. Login into the AIDEAS platform, establish a connection to an internal/external database, model the End-of-Life graph, and analyse it.
Objects¶
User: Represents the User interacting with the application.
Frontend: Represents the user interface and the presentation layer.
Backend: Represents the application logic and the server layer.
Database/Files: Represents the data or file storage layer.
Implementation Viewpoint¶
Description of implementation Component:¶
AI-LC is a tool in support of sustainable disassembly.
Technical Description of its Components:¶
Dependencies:
Development Language: - Python.
Libraries: Pandas, Networkx, Numpy, Matplotlib, Json.
Container: Docker.
Database need: MySQL.
Interfaces:
User Interface: WordPress.
Synchronous/Asynchronous Interface: RESTful APIs.
Network/Protocols: HTTP/HTTPS.
Data Repository: MySQL.
Requires:
Other AIDEAS Solutions: none
Solution architecture¶
![AI-LC[1360].drawio.png](_static%2Fimages%2FLC%2FAI-LC%5B1360%5D.drawio.png)
The development of the AI-LC tool will utilize the Python programming language, harnessing its capabilities in data science. To enable efficient data processing, popular libraries such as NumPy for array and matrix operations, Pandas for comprehensive data analysis, and Networkx for data manipulation using graphical techniques will be employed. Additionally, the Matplotlib library will be used for visualizing the data.
In terms of frontend development, the WordPress software will be utilized to create a user-friendly interface for AI-LC. Communication between the backend and frontend will be facilitated through a RESTful API, ensuring secure data transmission by implementing HTTPS protocols. The data collected and generated by the tool will be stored in a MySQL database.
To enhance software portability and simplify the deployment process, Docker will be employed. Docker provides a platform for packaging all the necessary dependencies and components required to ensure smooth execution of the software in various environments. By utilizing Docker, the deployment and setup of the AI-LC tool will be streamlined and efficient.